I will be going over the details of some issues encountered with the use of shorter springs. Part 1 of a 2 part post would explain the use of shorter length springs with a ride height adjustable coilover. Many consumers think that the use of a shorter length spring on a ride height adjustable coilover such as the Street Basis, Street Advance, Super Street, Basic’s, and Comfort Sport dampers would allow for the coilover to drop even further than the kits current maximum lowest setting. Essentially this is correct if the damper assembly has sufficient amount of range left on its body threads and/or overall damper length. Any consumer kits which have this type of set up will initially encounter the issue of the upper mount assembly riding against the bump rubber. This will eventually cause the bump rubber to break down causing either the damper to prematurely wear the seal and, in worst cases, cause internal damage of the damper. Other issues also experienced are spring slop (the spring moving out of its seat positions during operation due to the shortened length) damaging the damper body and threads, noises due to excessive damper component movement, and damper component failure (upper, lower spring seats, bushings, and bearings) from the loose fitting spring.
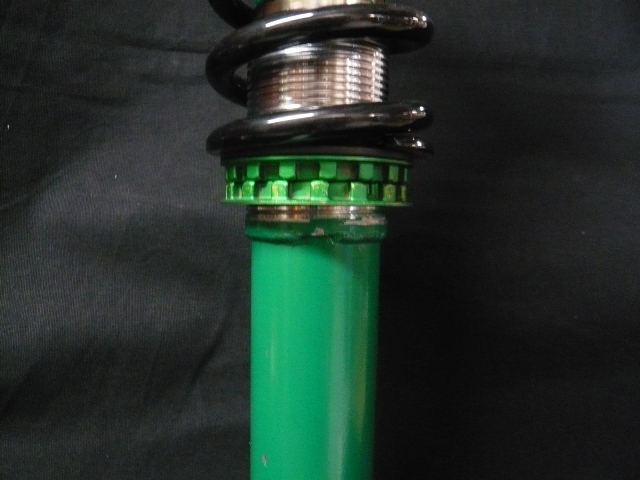
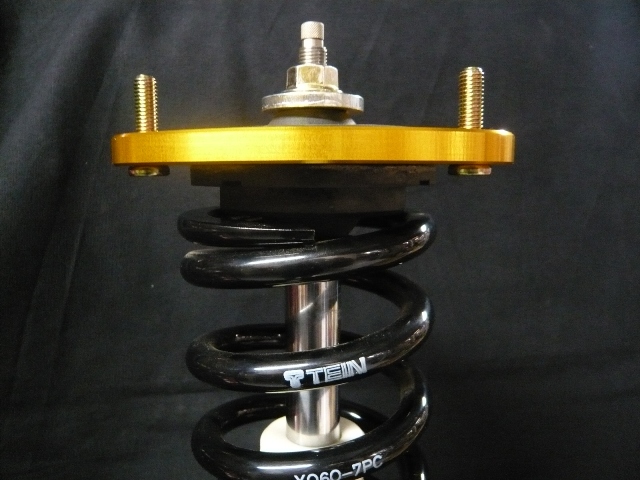
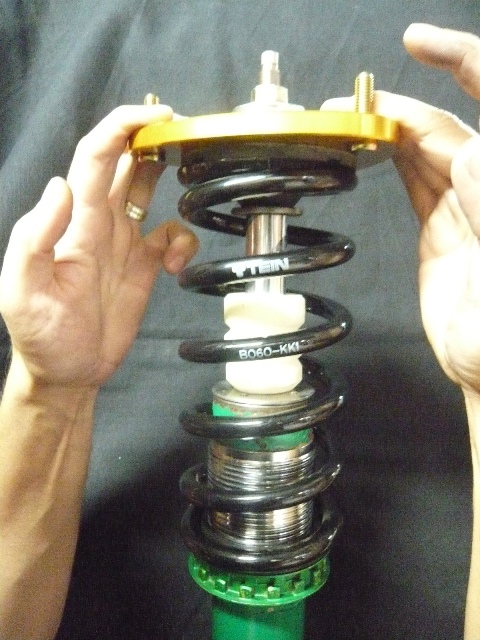
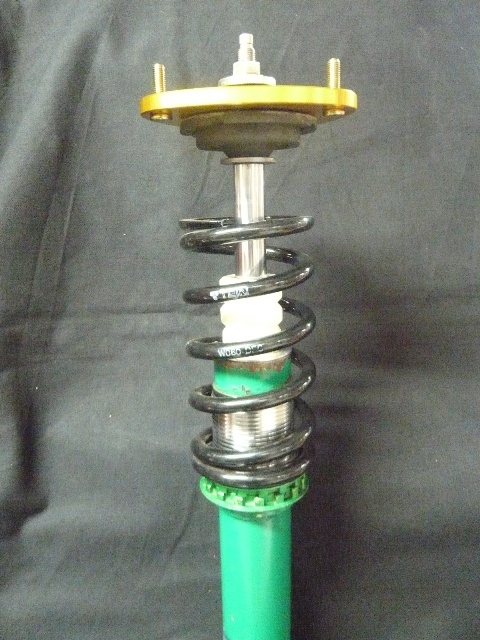
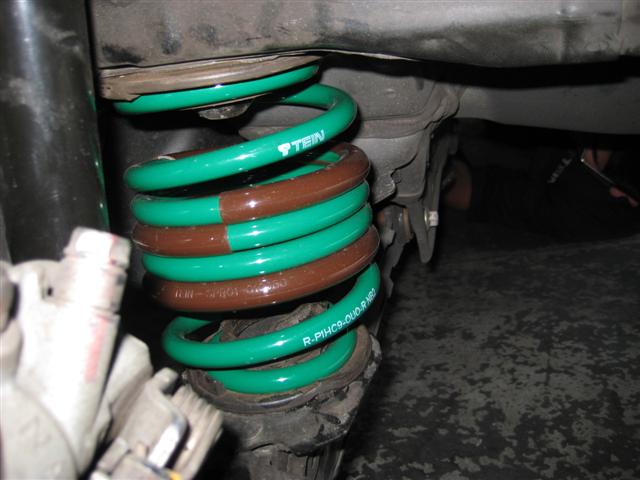
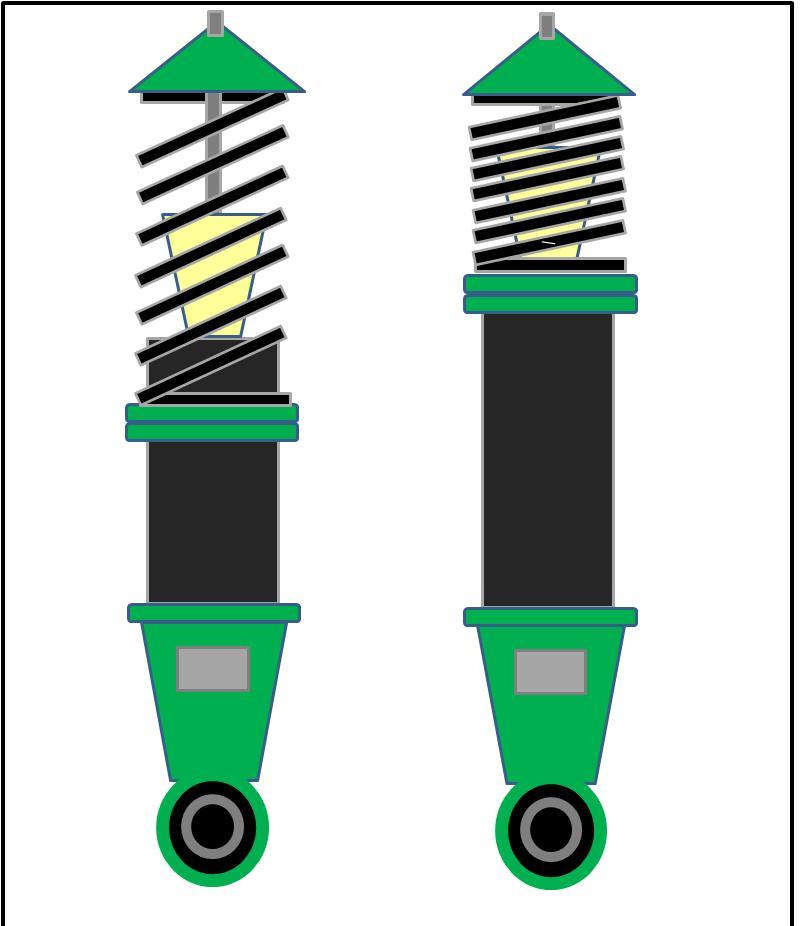
The images above shows a Super Street damper assembly from a 2004 Subaru Impreza WRX utilizing the standard 6KG spring rate with a 225mm length offered with the kit but set to a significantly low ride height. The second image above shows a load on mount assembly placed against the spring. This is not what the springs normal position would be with the vehicle weight added to it. For this application, the calculations of the spring rate (6KG) with the vehicles sprung weight (the weight above the spring excludes suspension components below the spring) (sprung weight is 235) which would compress the spring another 39mm placing the upper mount assembly closer to the bump stop.
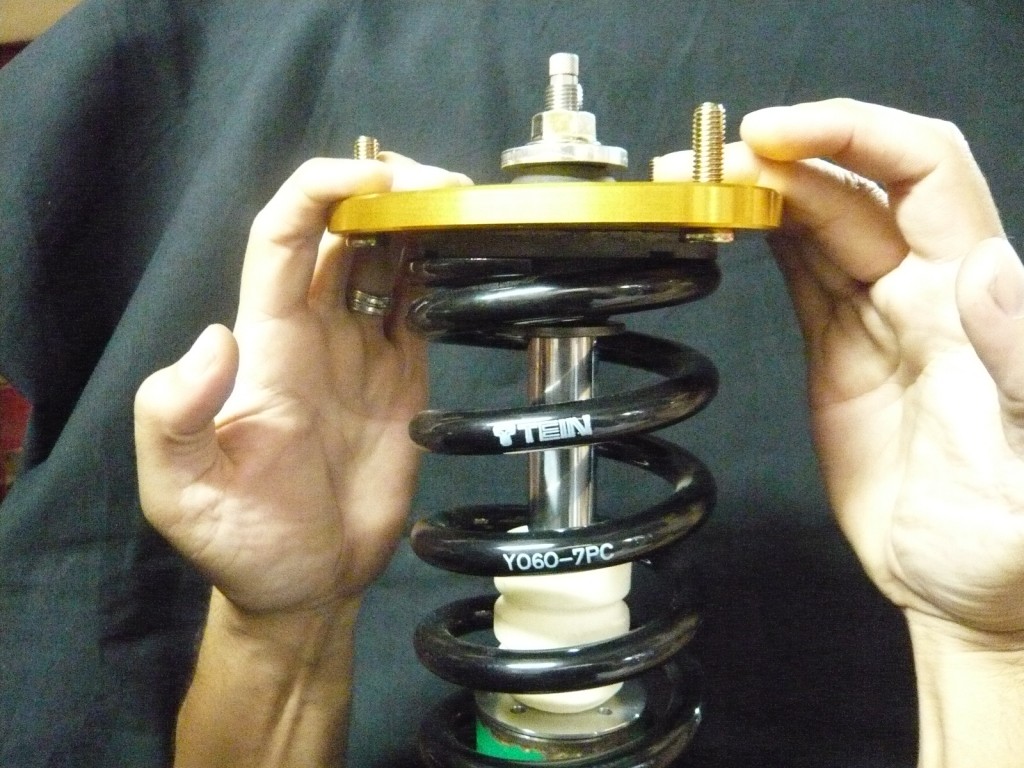
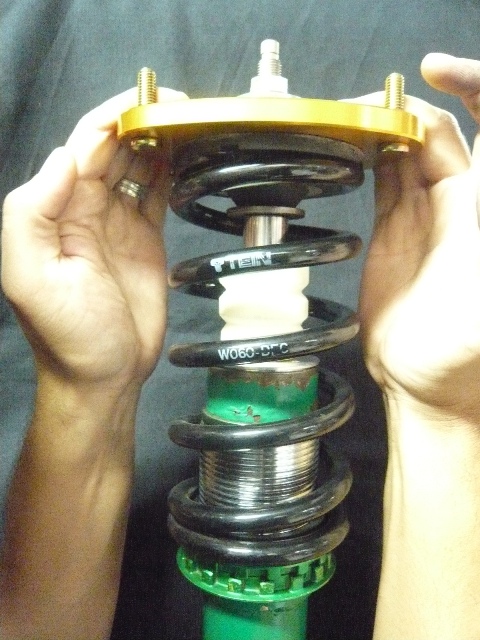
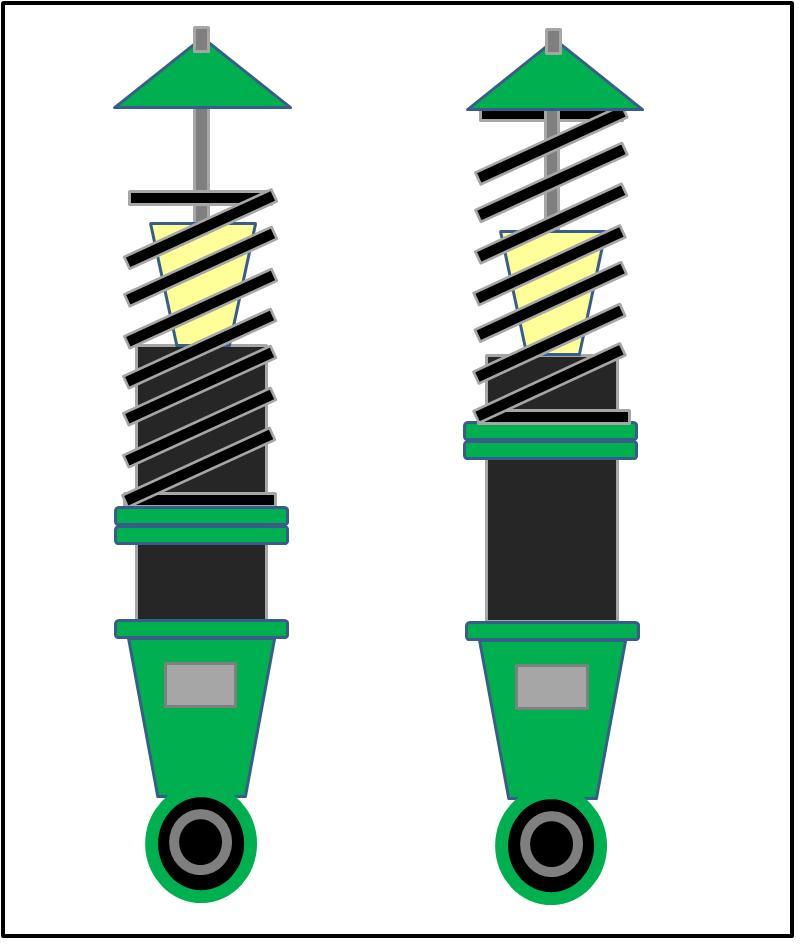
Now, if a consumer looking to utilize a 1 inch shorter length spring in the same spring rate, the images below shows (the same ride height setting is maintained) the increase in gap between the upper mount assembly as well as the amount of piston shaft stroke exposed. The second image below would show the dampers shaft compressed to the point at which the mount sit against the spring. With the previously mentioned sprung weight compressing the spring the additional 39mm’s the spring would compress further placing the upper mount assembly even closer to the bump stop eliminating stroke from the damper. At this point it would begin to hit the bump stop over slightly larger bumps on the road and slowly break down the bump stop.
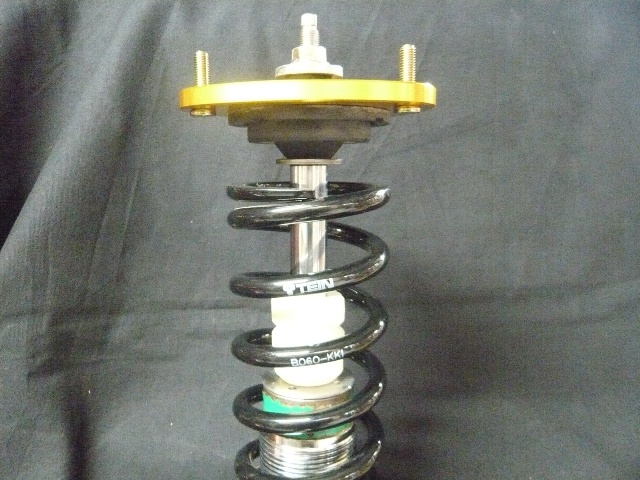
Now, should the consumer consider an even shorter length spring (in this case 2 inches shorter with the same spring rate; again, if the lowest ride height position is maintained), the images below show how the size in gap between the upper mount assembly and spring has immensely increased. The second image would again show the damper assembly compressed to the point at which the upper mount and spring meet. With the details previously mentioned of the sprung weight added to the spring, the upper mount would sit up against the bump stop with no type of real movement on the dampers stroke. The end result if utilized in this manner would be horrible ride quality, as their would be no stroke available, the upper mount assembly would immediately begin to damage the bump stop which in turn would either break the bump stop wedging the pieces into the seal portion and tearing at the seal or worst case splitting the bump stop apart allowing for the piston shaft to fully compress and hit the base of the damper damaging the unit internally.
The use of a stiffer spring in conjunction with a shorter length spring would be advisable as it would further support the vehicle weight minimizing the amount of contact between the upper mount assembly and bumper. This of course would also need to follow the spring rate change recommended range depending on the damper model. For any spring rate changes beyond our recommended range, we highly advise for the dampers to be sent in for a revalve service. Oversprung dampers can prematurely wear out as the dampers are not be able to keep up with the stiffer springs need for more rebound force.
For part 2 of the Short Spring Dilemmas, I will be going in depth to discuss full length adjustable coilover utilizing shorter lengths.